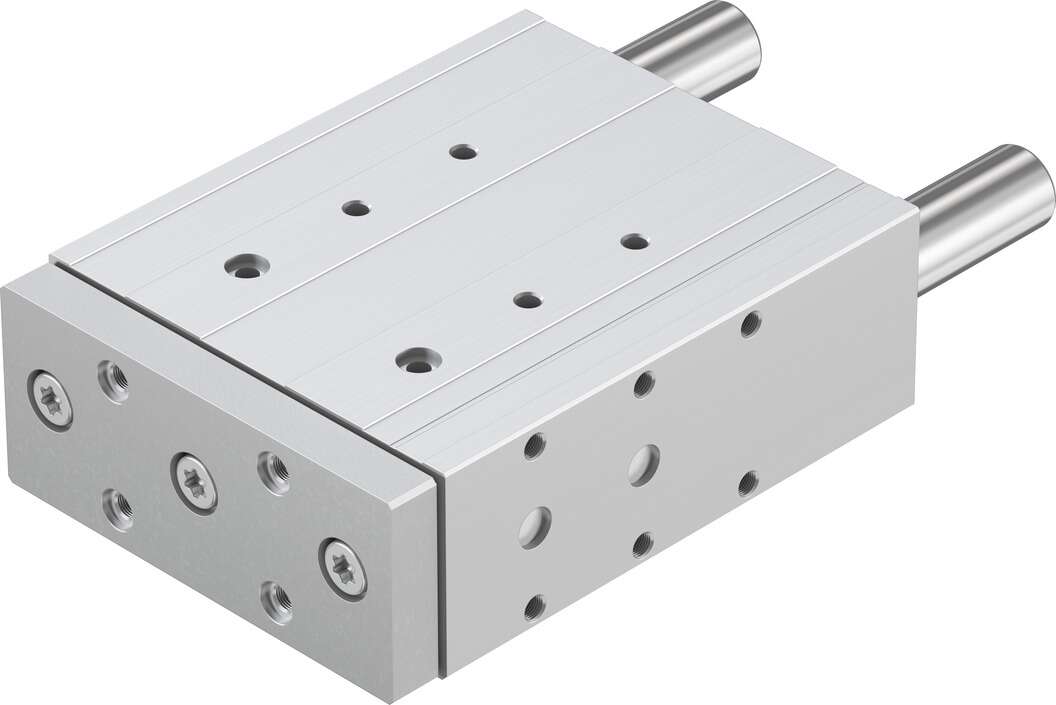
The festo directional cylinder DFM-16-50-P-A-KF, after a short return stroke, the light shield (6) triggers the photoelectric switch (2) to send a signal, which in turn controls the solenoid valve to reverse. The rodless cylinder continues to move forward after a short return stroke, surpassing the second station. During the forward movement, it activates the two-way three-way valve, which controls the pneumatic valve to reverse, causing the positioning post (4) to extend, preparing for the blocking plate and screws, etc., for shutdown and connection with other systems. 1, use a dial indicator to measure the bending value at various parts of the valve rod, and make marks and records, determining the highest and lowest points of bending. As shown in Figure 2, the fluid flow rate inside the solenoid valve is determined by the opening area of the piston inside the solenoid valve and the pressure difference, while the opening area of the piston inside the valve is determined by the balance of three forces. For example, if the local gap leakage at the joint surface is not very large, a copper mesh of 80~100 mesh can be used after heat treatment to reduce its hardness, then cut into the appropriate shape, placed on the leakage site of the joint surface, and then applied with cylinder sealant. If the gap at the joint surface is large and the leakage is severe, a groove of 50mm wide and 5mm deep can be cut on the upper and lower joint surfaces, and an IGr18Ni9Ti toothed gasket can be embedded in the middle. The thickness of the toothed gasket is generally 0.05~0.08mm larger than the depth of the groove, and an equivalent shape stainless steel gasket can be used for adjustment. Common fault locations and cause analysis of solenoid valves The quality of solenoid valve operation performance will directly affect the working quality of the entire control system. Since the solenoid valve is in direct contact with the medium being adjusted on-site, the working environment is very harsh, thus prone to various faults. During production, in addition to promptly eliminating these faults, regular maintenance and periodic inspections must also be carried out. Especially for solenoid valves used in particularly harsh environments, maintenance and periodic inspections should be given more attention. 2, joints are generally connected in parallel in the system's branch to function as pressure regulation, pressure stabilization, and pressure reduction, while the pressure reducing valve is generally connected in series in a certain branch to function as pressure reduction and pressure holding for that branch! The relief valve is normally closed and only acts when the system is overpressured; the pressure reducing valve is normally open and reduces pressure through a narrow passage. The function of the relief valve is: pressure stabilization, overflow, and overload protection. The function of the pressure reducing valve is to reduce pressure, reducing the pressure in a certain part of the hydraulic system. They have different uses and therefore cannot be substituted for each other. The flow range controlled by electric cylinders of different diameters is different. When selecting valves, the valve internal pipeline system design flow should be taken in the best working area on the larger side of the valve control flow range according to the valve working characteristic curve. If the selected valve port diameter is too small, the valve will work at the high end of its control flow range, which can easily cause noise. If the selected valve port diameter is too large, the valve will work at the low end of its control flow range, causing too large a variation in system flow, which can easily cause hydraulic imbalance in the valve external pipeline system and also cause economic waste. Generally, the electric cylinder diameter is equal to or one size smaller than the interface pipe diameter of the valve internal pipeline system is better. The main advantages of the festo directional cylinder DFM-16-50-P-A-KF are small size, reliable action, convenient maintenance, and low price. When choosing, it is necessary to pay attention to selecting the normally open or normally closed type according to the process requirements. 3, installation
Guided Cylinder DFM-16-50-P-A-KF belongs to the Air Pressure Cylinders series under CKD company, model number DFM-16-50-P-A-KF. To purchase or inquire about Guided Cylinder DFM-16-50-P-A-KF, you can directly contact 158 0047 0089 (Mr. He).