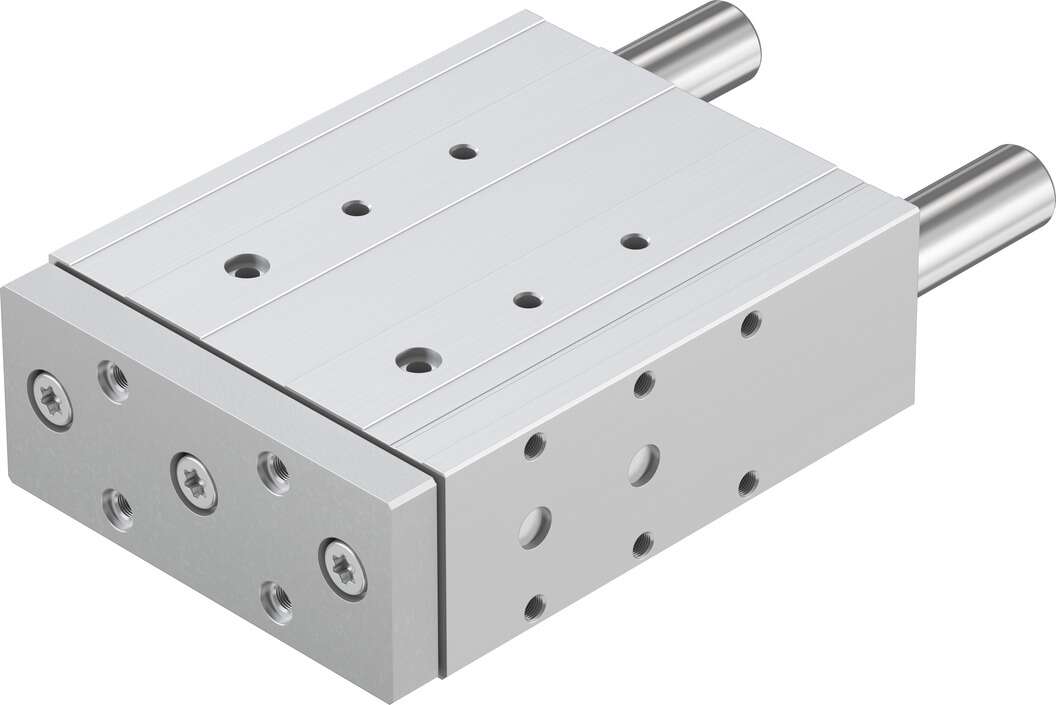
The festo directional cylinder DFM-32-100-P-A-GF piston rod replacement process; buffer capacity ADN-...-P, advantage no adjustment saves time, advantage no adjustment buffer capacity is four times that of ADN-...-P saves time and reduces noise, compact cylinder ADN, in line with ISO21287 main features, modular product system derivative type symbol main features brief description S1 reinforced piston rod increases lateral force. The lateral force it can absorb is several times that of a basic cylinder, S2 double-ended piston rod used for work at both ends, the force of the advancing and returning strokes is the same, used for installing external stops, S6 high-temperature resistant seals can withstand up to 120°C, S10 piston low-speed constant speed motion (slow) suitable for constant, non-jerky speed motion throughout the entire stroke of the cylinder. Seals contain silicone oil (contains paint wetting defect material) S11 low friction special seals can greatly reduce system wear. This is equivalent to greatly reducing the response pressure. Seals contain silicone oil (contains paint wetting defect material), S20 double-ended hollow piston rod used for supplying vacuum, small parts, media, etc., K2 extended piston rod external thread -, K5 special piston rod thread metric standard thread in accordance with ISO, K8 extended piston rod -, K10 smooth anodized aluminum piston rod specifically for welding environments: - anti-weld spatter - low workload - higher surface hardness compared to steel - long service life KP with clamping device piston rod integrated clamping device, EL with end position lock positively locks the end position, as drop protection. If a pressure drop occurs, the piston rod is fixed in the end position protective conduit system installation method and maintenance method; valve is a dual-piston pressurizing device specifically for compressed air. When using compressed air to pressurize, the integrated one-way valve will automatically accelerate the pressurization of the second side. The output pressure p2 can be increased to twice the air source pressure p1. The required output pressure is set by the hand-controlled pressure regulating valve. If the pressure boosting valve does not have a pressure regulating valve, the output pressure is twice the air source pressure. The air source for both driving pistons is controlled by a pneumatic directional control valve, and upon reaching the end position of the stroke, the directional control valve will automatically reverse. After ventilation, if the required output pressure is not reached, the pressure boosting valve will automatically start. When the required output pressure is reached, the pressure boosting valve will switch to energy-saving mode. Once a pressure drop occurs during system operation, the pressure boosting valve will automatically restart. For the DPA with sensing option, the single stroke of the driving piston can be recorded through external sensors and cumulative counters. -H- Note that the pressure boosting valve is only used for air source pressure regulation when necessary and is not suitable for replacing an air compressor, as continuous operation will greatly increase the wear of the seals and driving pistons. (4) Leakage. Leakage can cause insufficient air pressure, making it difficult for the forced valve to open and close, due to damage to the sealing gasket or wear of the sliding valve causing several cavities to communicate with each other. When dealing with the failure of the switching system's gripper, the appropriate time should be chosen, and the gripper should be handled when it is de-energized. If it cannot be completed within a switching gap, the
Guided Cylinder DFM-32-100-P-A-GF belongs to the Air Pressure Cylinders series under CKD company, model number DFM-32-100-P-A-GF. To purchase or inquire about Guided Cylinder DFM-32-100-P-A-GF, you can directly contact 158 0047 0089 (Mr. He).