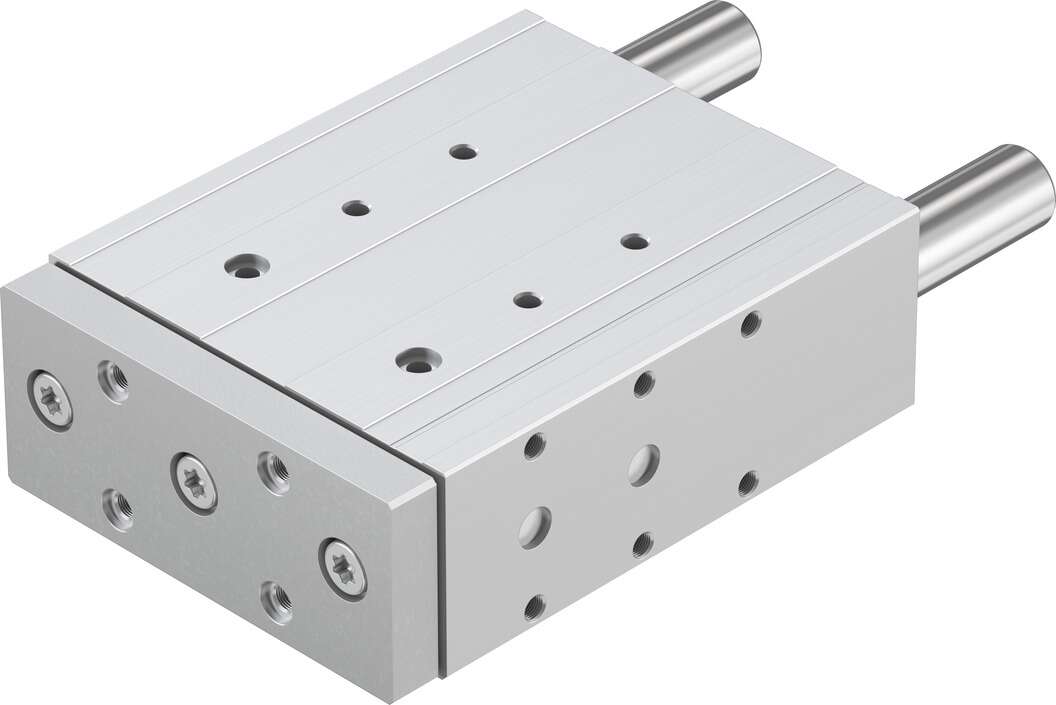
The
festo directional cylinder DFM-40-125-P-A-KF valve has a larger port diameter, which becomes more significant when the pressure water entering the control chamber above the diaphragm (piston) is discharged into the atmosphere or downstream low-pressure area. The pressure value acting on the bottom of the valve flap and below the diaphragm is greater than the pressure above, thus pushing the main valve flap to a fully open position. When the pressure value in the control chamber above the diaphragm (piston) is between the inlet pressure and the outlet pressure, the main valve flap is in an adjusting state, and its adjustment position depends on the combined control action of the needle valve and the pilot valve in the conduit system. The pilot valve can open or close its own small valve port by changing the downstream pressure, thereby changing the pressure value in the control chamber above the diaphragm (piston) and controlling the adjustment position of the main valve flap. It can be used for domestic water supply, fire-fighting systems, and industrial water supply systems. A brief analysis of the operating principle and selection skills of condensate discharge devices; condensate discharge devices can be classified into three major categories based on the measurement method (detection target object) of the simulated photoelectric sensor: transmission (absorption) type, diffuse reflection type, and occlusion type (beam blockage). The so-called transmission type refers to the measured object being placed in the optical path, with the light energy emitted by the constant light source passing through the measured object, some of which is absorbed, and the transmitted light is projected onto the photoelectric element; the so-called diffuse reflection type refers to the light emitted by the constant light source being projected onto the measured object, then reflected from the surface of the measured object and projected onto the photoelectric element; the so-called occlusion type refers to when the light flux emitted by the light source is partially blocked by the measured object, changing the light flux projected onto the photoelectric element, the degree of change is related to the position of the measured object in the optical path. The photodiode is the most common type of light sensor. 3. Self-sealing valve cover The valve cover and valve body are designed with a self-sealing structure, and within the allowable pressure range, the higher the fluid pressure, the tighter the seal. How does the proportional valve work; proportional pressure reducing valve VPPE – 5, 2 Proportional pressure reducing valve with display VPPE...E1 – 8, 3 Setting point module MPZ is used to generate 6+1 analog voltage signals 11, 4 Digital input/output – used to drive the setting point module –5 With cable socket SIM-M12-5GD-...-PU with straight-through socket, used to drive VPPE...E1 11, 6 With cable socket SIM-M12-4GD-5PU with straight-through socket, used to drive VPPE, 7 With cable socket SIM-M12-4WD-5PU with right-angle socket, used to drive VPPE, 8 Socket SIE-GD straight-through socket, rated diameter, pressurized 11 mm, rated diameter, exhaust 12 mm Drive type Electrical, sealing principle Soft assembly position arbitrary, design structure pilot-controlled piston-type pressure reducing valve, short-circuit strength for all electrical interfaces, safety operation guide MPPES safe position, polarity fault tolerance protection for all electrical interfaces, valve function 3-position normally closed proportional pressure reducing valve, pressure control range 0 ... 6 bar Input pressure 1 7 ... 8 bar, maximum pressure hysteresis 0.05 bar Switching time, closed
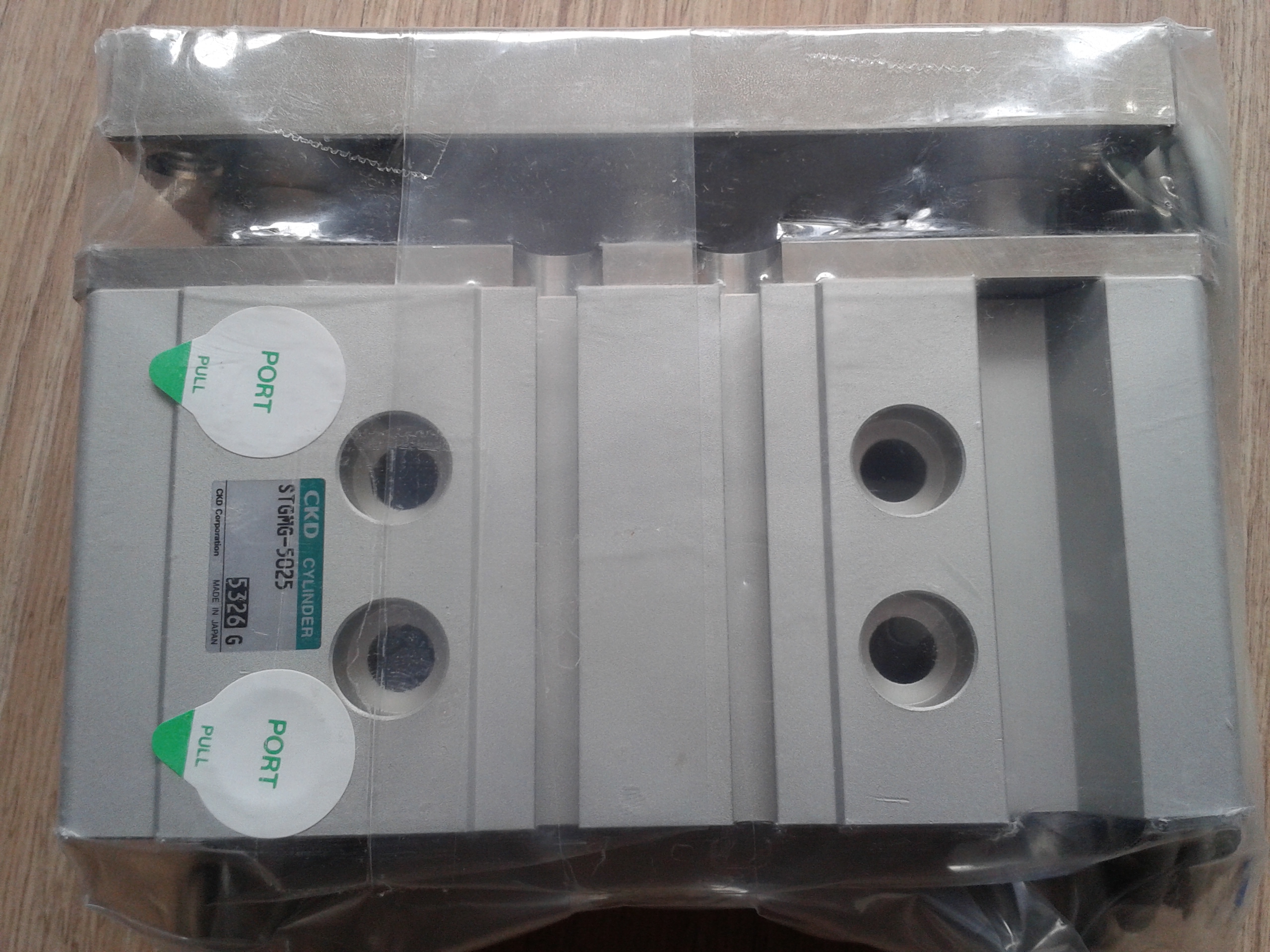
Guided Cylinder DFM-40-125-P-A-KF belongs to the Air Pressure Cylinders series under CKD company, model number DFM-40-125-P-A-KF. To purchase or inquire about Guided Cylinder DFM-40-125-P-A-KF, you can directly contact 158 0047 0089 (Mr. He).