The replacement method for the locking cylinder CAC4-A-63-50-Y involves replacing defective parts either entirely or partially. This method is widely used in the maintenance of construction machinery, and its key lies in identifying the parts that have issues. Once the problem is found, a new, identical part can be installed, and typically, this will allow the valve to function normally. Common reasons for electromagnetic valve failure include excessive wear of the valve's sealing components and breakage of the valve core displacement sensor probe, while the integrated amplifier rarely causes problems. Throttle valves are sensitive to pressure changes; they open very quickly to reach their maximum state and expel anything that exceeds the range, usually used for compressible materials. 1. Design options MEDAN rodless cylinders can be provided as a basic module, and according to application requirements, guide devices, locking devices, or both can be selected. The sensitivity and reliability of electromagnetic valve action refer to how sensitive the electromagnetic valve is to changes in medium parameters and how it responds accordingly. For valves such as throttle valves, pressure reducing valves, regulating valves, etc., used to adjust medium parameters, and safety valves, drain valves, etc., with specific functions, their functional sensitivity and reliability are very important technical performance indicators. The service life of electromagnetic valves indicates their durability, which is an important performance indicator of valves and has significant economic implications. It is usually expressed in the number of opening and closing cycles that can ensure the sealing requirements, or it can be expressed in terms of usage time. 4. Electromagnetic valve stem diameter: For multi-turn type rising stem valves, if the electric device allows the stem diameter to pass cannot pass through the stem of the valve it is paired with, it cannot be assembled into an electric valve. Therefore, the inner diameter of the electric device's hollow output shaft must be larger than the outer diameter of the stem of the rising stem valve. For part-turn valves and multi-turn German electromagnetic valves with concealed stems, although the stem diameter passing issue does not need to be considered, when selecting, the stem diameter and key slot size should be fully considered to ensure normal operation after assembly. The minimum working pressure difference above 0.04Mpa can use indirect pilot type; the minimum working pressure difference close to or less than zero must use direct acting or step direct type. 3. Cylinder valves can choose needle valves, instrument valves, sampling valves, pressure gauge valves, etc. As shown in Figure 2, the flow rate of the fluid inside the electromagnetic valve is determined by the opening area of the piston inside the electromagnetic valve and the pressure difference, and the opening area of the valve piston is determined by the balance of three forces, such as: how the basic valve controls the hydraulic or pneumatic cylinder system as shown. The working hole of the single electric control two-position four-way (five-way) electromagnetic valve has one that is normally open. When the electromagnetic valve is in the de-energized state, the medium from the inlet (liquid) hole P directly enters the working hole B, causing the hydraulic or pneumatic piston to push towards the C end. At the same time, it presses down and rotates the exposed manual device to block the manual device, 1 push out the aluminum plate 2 rotate the aluminum plate 180° and position, 3 block the manual device pilot exhaust, used for valves with V-shaped electromagnetic coils, remove the sealing pad on the top cover, the mark 3 on the cover must always be aligned with the valve body.
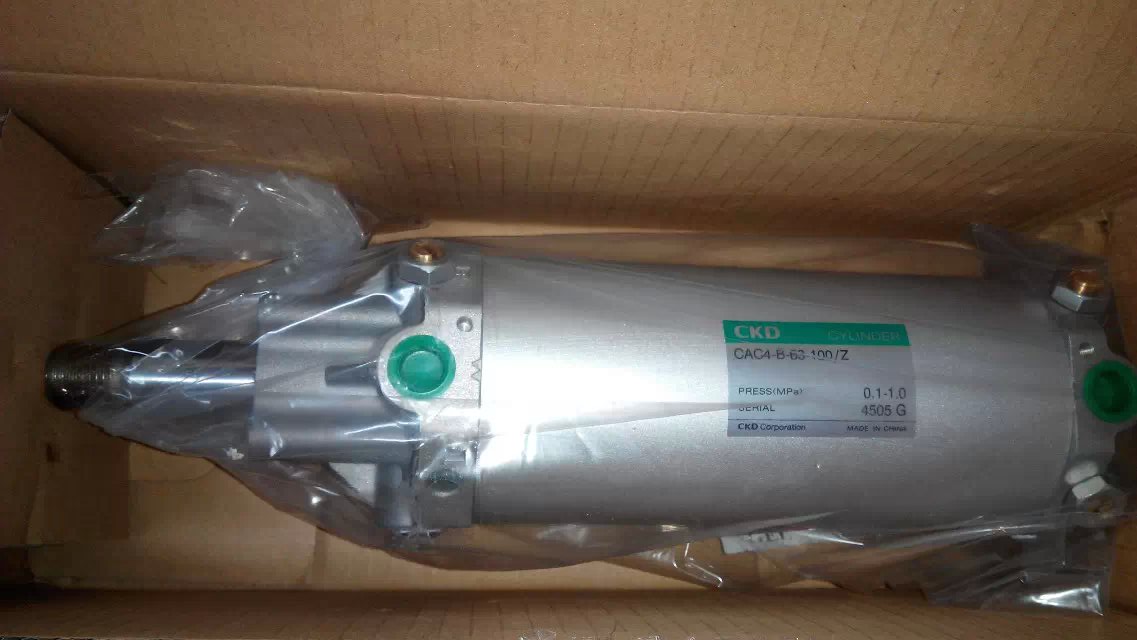
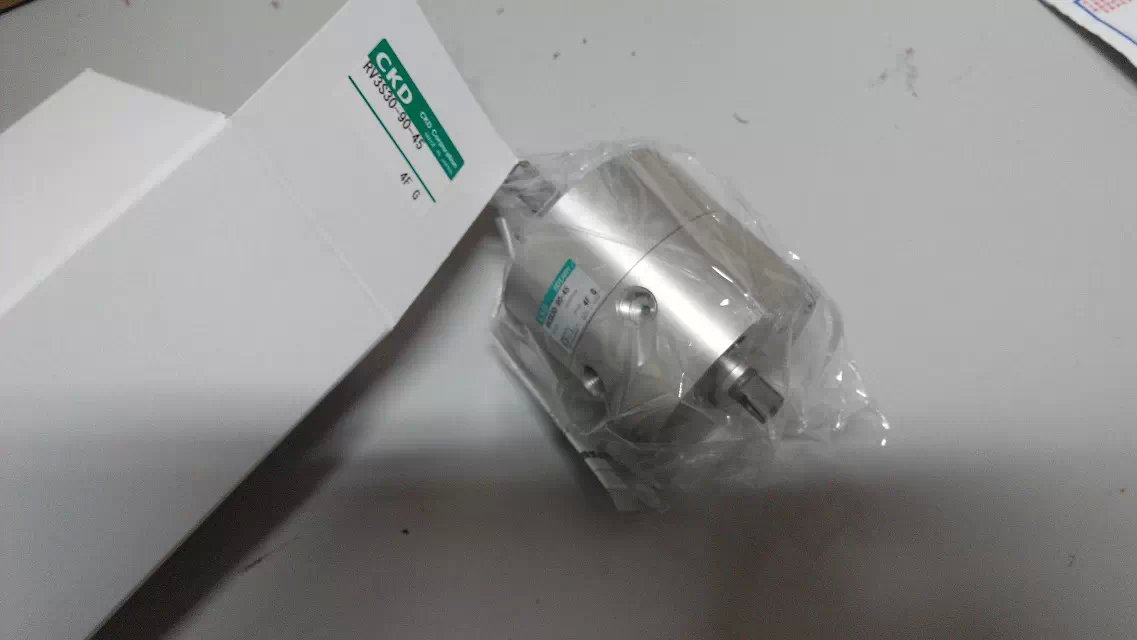
Locking cylinder CAC4-A-63-50-Y belongs to the Air Pressure Cylinders series under CKD company, model number CAC4-A-63-50-Y. To purchase or inquire about Locking cylinder CAC4-A-63-50-Y, you can directly contact 158 0047 0089 (Mr. He).