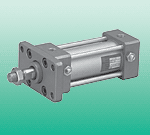
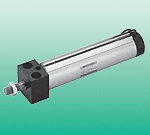
The amount of SCA2-T-63/Z packing added should be appropriate and leave room for re-pressing. The depth to which the gland is pressed into the stuffing box should not be less than the height of the stuffing box, nor should it be greater. When tightening the packing gland, the force applied to the screws should be even. It is best to turn the valve stem while tightening the packing to check the degree of packing tightening on the gate rod. After the gland is tightened, it should be flat and without any tilting. For installation of formed packing, methods that can be directly套入 on the upper end of the valve stem should be used as much as possible. When the packing cannot be directly套入, the method of cut-in lap can also be used. Introduction to the structure principle and characteristics of the cylinder; the main advantage of the cylinder spring change is the direct participation in the control valve and the indirect influence to improve the sensitivity of the method and the life of the main valve housing plug, double shell, with high precision, good reproducibility, rapid operation after the back seat, no escape, high back pressure discharge, long-term work they are mainly used in oil and gas, chemical, electrical, metal, and city gas compressors, containers, overpressure protection pipe equipment. The sealing surface is generally made of metal materials, even after precise processing, it is difficult for the valve to achieve sealing. The situations that cause leakage of the valve sealing surface are very complex. 116B-122JD, E-92050-01-02434B-L00-GFG0-1KJ, E-92050-02-024111B-131BA, 451A-D0A-DM-DDAJ-1JB250B-111BAAA, 55B-14-PI-111JJ35A-AAB-DDAA-1BA M0D:R025, 45A-GC1-DAAJ-1KA82A-0A-CAA, 411A-D0A-DM-DFFJ-2JB36A-B00-JDC0-1KJ M0D:0650, 451A-D0A-DM-DFFJ-2JB36A-B00-JDC0-1KA M0D:EH43, 56C-16-501JB36A-E00-JDC0-1KA M0D:EC87, 57D-76-111JA M0D:040552A-14-F0A-DM-DDAJ-2KD, 34B-L00-GFGA-1KA M0D:R02052A-11-B0A-GM-GEMF-1KA M0D:3629, 55B-14-PI-501JJ421A-D0A-DM-DDFJ-1KJ, 35A-ACA-DABA-1BAM-42004-06, 35A-ACA-DDAA-1BA42A-000-LN2, 45A-BC1-DDAA-1BASM16-DNA-0AA-00M-1A-42 M0D:7277, 47A-SD0-HDAA-1BA42A-FME-000-GDDP-3GA M0D:7256, 55B-14-PI-501BA42A-000-LN1, 56C-58-RA42A-000-LJ2, 58D-56-RA42A-BME-000-GDDP-0
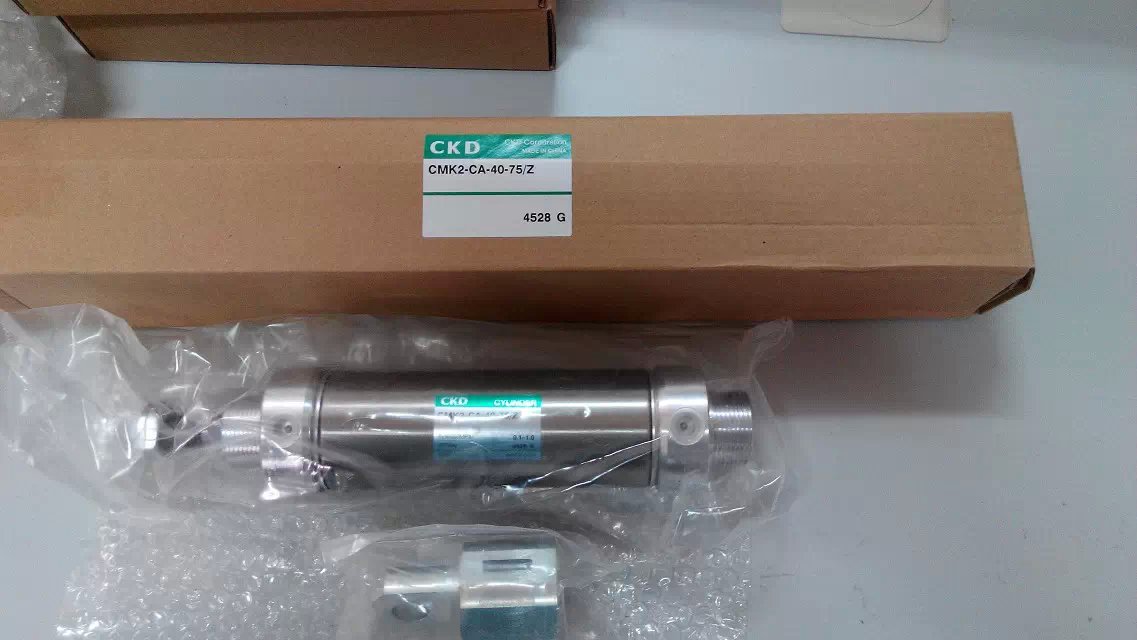
Medium-sized cylinder SCA2-T-63/Z belongs to the Air Pressure Cylinders series under CKD company, model number SCA2-T-63/Z. To purchase or inquire about Medium-sized cylinder SCA2-T-63/Z, you can directly contact 158 0047 0089 (Mr. He).