How to handle the overload of the CMK2-FA-20-100-T0H-D solenoid valve; the corresponding solenoid coil aJ, the NDV blanking plate is used for sealing the empty air path plate base aA, the throttle plate GRO is suitable for ISO sizes 1, 2, and 3, and integrates exhaust throttling at ports 3 and 5. The throttle plate is installed between the valve and the individual base/air path plate base. aB, the intermediate pressure reducing plate LR-ZP is suitable for ISO sizes 1, 2, and 3, and is used to adjust the pressure from 0 to 10 based on the air source pressure. The intermediate pressure reducing plate is installed between the valve and the individual base/air path plate base. Valve function two-position five-way, single solenoid control Structural features spool valve Sealing principle soft Drive method electric Reset method mechanical spring or pneumatic spring Pilot control method pilot control Pilot air source internal or external pilot Flow direction unidirectional Exhaust function with flow control Manual device through accessories, locked Installation method through-hole mounting, N1 type solenoid coil Electrical interface plug, square structure, conforms to EN175301-803 standard, type A, Material description models without copper and polytetrafluoroethylene Ordering data, without N1 type solenoid coil 1)MN1H-5/2-D-1-C without type solenoid coil Pilot air source. Vacuum suction cup ESV-80-SU, double-acting anti-twist cylinder DZH-16-25-PPV-ADFM-25-30-P-A-GF, EMME-AS-60-S-LS-AMXLFRS-3/8-D-MINI-A, pressure reducing valve LR-M3-G1/2-07GIKM series pressure reducing valve LRB-M2-G1/2-07, AEVULQ-40-20-P-A-S26,187330 MPPES-3-1/2-6-010, DSM-10-240-P-A-FF, double-acting anti-twist cylinder DZH-25-40-PPV-A, air tube PUN-10X1,5-S-2-SWMS4-LFR-1/4-D7-ERV-AS, pressure reducing plate LR-ZP-A-D-3-CT pressure reducing valve LR-1/4-D-MINI, AEVULQZ-25-15-A-P-AAEVULQZ-32-30-P-A-S6, DSM-6-180-P-A-FF, hydraulic buffer YSR-20-25 polyurethane air tube PUN-E-4X0,6-BL-500, D series lockable pressure reducing valve LRS-1/8-D-7-MINID series pressure reducing valve LR-1/2-D-7-O-I-MIDI, GRLA-1/8-QS-4-RS-DAEVULQ-50-25-P-A-S2, DSBC-50-50-PPSA-N3DSBC-125-160-PPVA-N3, DGC-K-80-300-PPV-A-GK, air tube PUN-10X1,5-S-1-BL
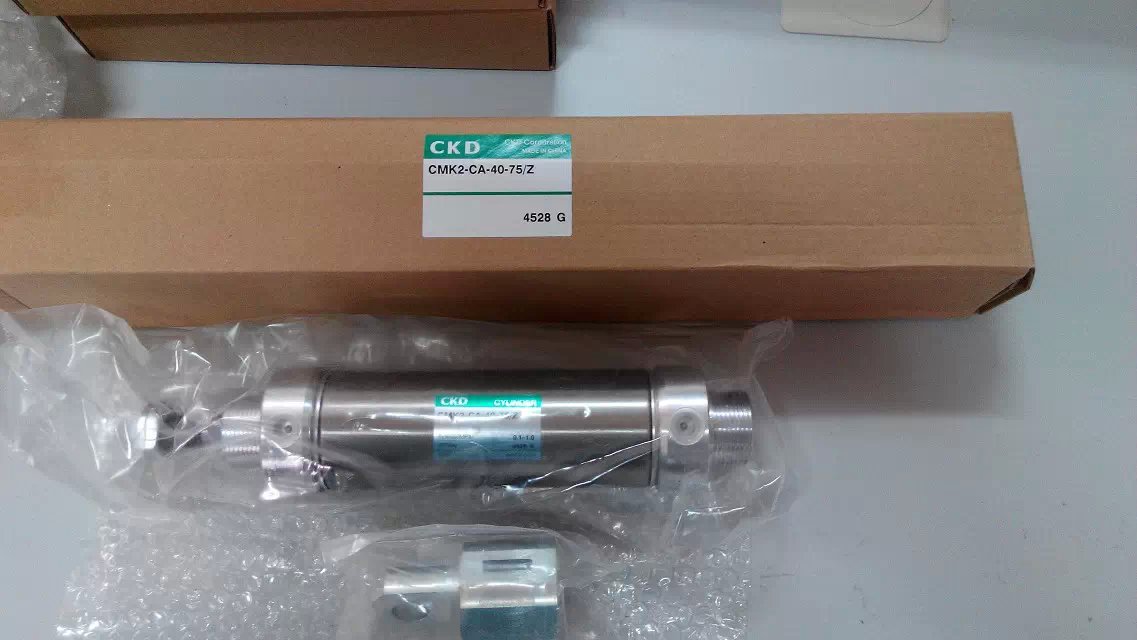
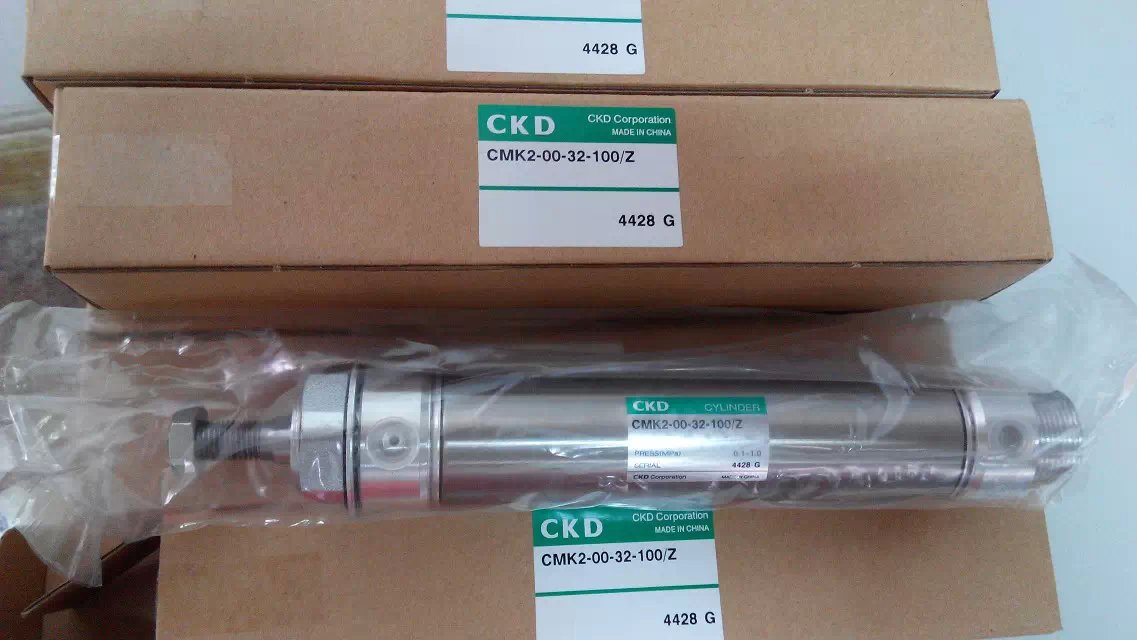
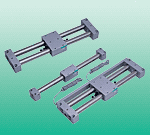
Double acting cylinder CMK2-FA-20-100-T0H-D belongs to the Air Pressure Cylinders series under CKD company, model number CMK2-FA-20-100-T0H-D. To purchase or inquire about Double acting cylinder CMK2-FA-20-100-T0H-D, you can directly contact 158 0047 0089 (Mr. He).