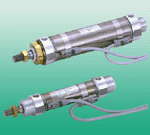
The CMK2-G-FA-32-75-T2H3-D meets the accuracy requirements of the entire electronic scale. An electronic scale mainly consists of a scale body, proximity switch, and instrument. When choosing the accuracy of the proximity switch, the accuracy of the proximity switch should be slightly higher than the theoretical calculated value, because the theory is often limited by objective conditions, such as a slightly weaker scale body, not very good instrument performance, and harsh working environment of the scale, all of which directly affect the accuracy requirements of the scale. Therefore, requirements need to be improved from all aspects, while also considering economic benefits to ensure the goal is achieved. Fast action, low power consumption, and compact size make the electromagnetic valve's response time as short as a few milliseconds, even pilot-operated electromagnetic valves can be controlled within tens of milliseconds. Due to its self-contained circuit, it reacts more sensitively than other self-controlled valves. A well-designed electromagnetic valve coil power consumption is very low, belonging to energy-saving products; it can also achieve that once triggered, the valve position is automatically maintained, and it does not consume any power at all when idle. The electromagnetic valve has a small size, saving space and being light and elegant. DSBC-32-300-D3-PPSA-N3, DGC-K-50-1100-PPV-A-GK polyurethane air tube PUN-10X1,5-SG-6-BL-1/4, pressure reducing valve LR-M2-G1/2-10GI pressure reducing valve LR-M3-N3/8-10GK, GRLA-M3AEVULQ-20-5-A-P-A, DSBC-80-30-PPVA-N3, DSM-16-270-CC-A-B, pressure reducing valve LR-M2-N1/2-16GEMME-AS-60-M-LS-AMX, GRLA-M5-QS-4-LF-C pressure reducing valve LR-1/2-D-MAXI, DSBC-63-250-D3-PPSA-N3 vacuum suction cup VAS-30-1/8-SI, air tube PUN-6X1-S-6-BL double acting multi-mount DMM-10-15-P-A, pressure reducing valve LR-M2-N3/8-16GILFR-1/4-D-MINI-KF-A, DSM-10-180-P-A pressure reducing valve LR-M1-G1/4-10I, polyurethane air tube PUN-6X1-GN vacuum suction cup ESV-30-SU, pressure reducing valve LR-M3-N3/4-10GIDFM-100-100-P-A-GF, vacuum suction cup ESV-30-EU pressure reducing plate LR-ZP-B-D-1-CT, EMME-AS-100-M-HS-AMX pressure reducing valve LR-M3-G3/4-07, D series lockable pressure reducing valve LRS-1-D-O-MAXIDSBC-32-50-D3-PPSA-N3, 161170 MPPE-3-1/4-6-420-B pressure reducing valve LR-M3-N3/4-04, pressure reducing valve LR-M2-G1/2-07AEVULQZ-80-20-A-P-A, AEVULQZ-20-20-P-A, double acting multi-mount?DMML-32-25-P-A, double acting anti-twist air
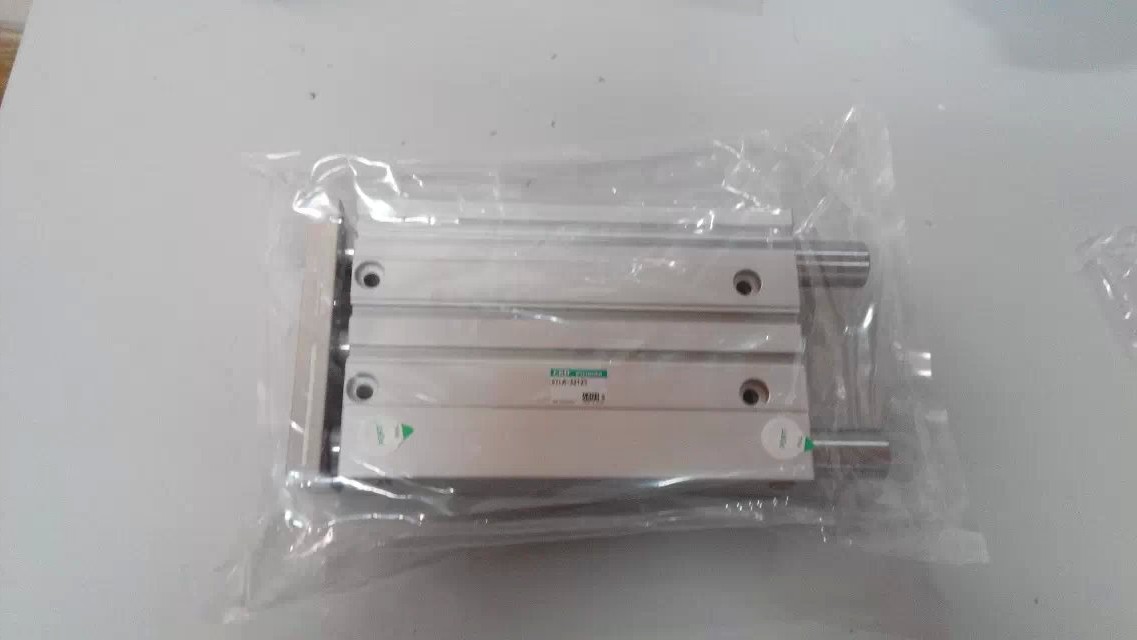
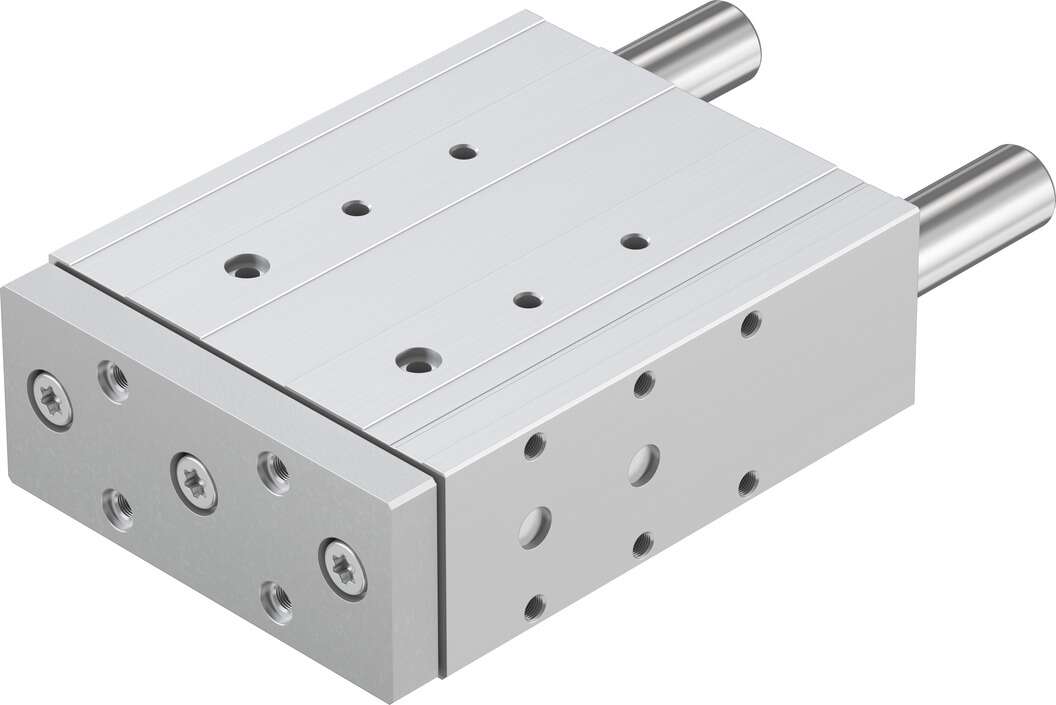
Double acting cylinder CMK2-G-FA-32-75-T2H3-D belongs to the Air Pressure Cylinders series under CKD company, model number CMK2-G-FA-32-75-T2H3-D. To purchase or inquire about Double acting cylinder CMK2-G-FA-32-75-T2H3-D, you can directly contact 158 0047 0089 (Mr. He).