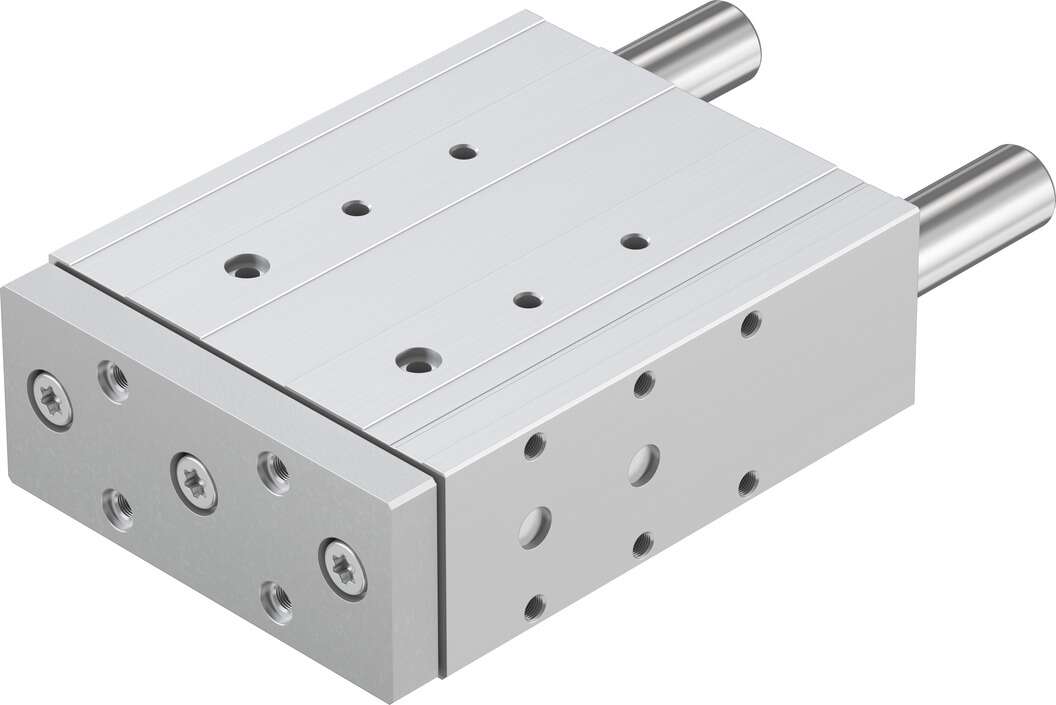
festoGuide cylinderDFM-50-50-P-A-KF The pilot-operated two-position four or five-way basic valve is not interchangeable between gas and liquid media due to differences in structure and sealing forms. When the basic valve is powered off, the closing element will return to its original position, causing the solenoid valve to close. During this action, the direct up-and-down movement of the armature can achieve the on-off operation of the solenoid valve medium, hence it is also known as a basic valve. (Note: Normally closed solenoid valves open when powered on and close when powered off; normally open solenoid valves close when powered on and open when powered off.) The nominal size of the basic valve is not greater than DiVIO. When the coil of a small-diameter direct-acting solenoid valve is energized, the magnetic circuit generates electromagnetic force, lifting the armature and overcoming the return spring force to open the valve seat, allowing the working medium to flow through the pipeline immediately. When the coil is de-energized, the electromagnetic force disappears, and the armature falls due to its own weight and spring force, sealing the valve seat and cutting off the flow of the working medium through the pipeline. Soft-start valves belong to the category of automatic valves and are also important safety accessories for limiting and relieving pressure on special equipment such as boilers, pressure vessels, and pressure pipes. How should the replacement of the packing for the blocking cylinder be handled? 1. Instantly brake the workpiece carrier through the piston rod. 2. Activate the cylinder to release the workpiece carrier. 3. With the force of the spring or air pressure, the piston rod extends again until the roller contacts the workpiece carrier. The workpiece carrier continues to move forward. 4. After the workpiece carrier passes, the piston rod extends to the terminal position. Stop the next tool carrier. Model, single-acting or double-acting, STA stop cylinder, STAF stop cylinder, with flange mounting parts, cylinder diameter ? [mm] stroke [mm] buffer, P with elastic buffer ring/pad at both ends position sensing, A through proximity switch typeR roller type, proximity switch SME/SMT-8, can be integrated into the cylinder barrel 30, 2 groove cover ABP is used to prevent dust from entering, cylinder diameter ? 20 32 50 80, cylinder diameter STA M5 Gx Gx -, STAF - M5 Gx Gx, stroke [mm] 15 20 30 30/40, piston rod ? [mm] 12 20 32 50, working pressure [bar] 10, working medium filtered compressed air, lubricated or unlubricated structural features piston cylinder, with mechanical reset buffer, both ends with elastic buffer ring/pad, position sensing through proximity switch, installation method through through hole, through internal thread, installation position arbitrary, working mode single-acting or double-acting. Anti-torsion two-sided flat piston rod Ambient temperature1) [°C] +5 ... +601) Note: Proximity switch operating range. -H- Note: This product complies with ISO 1179-1 and ISO 228-1 standards. Force [N] Cylinder diameter ? 20 32 50 80. Stroke 15 20 30 30 40. Allowable impact force on the extended piston rod 170 830 2,300 14,600 13,300. Spring force 1
Guided Cylinder DFM-50-50-P-A-KF belongs to the Air Pressure Cylinders series under CKD company, model number DFM-50-50-P-A-KF. To purchase or inquire about Guided Cylinder DFM-50-50-P-A-KF, you can directly contact 158 0047 0089 (Mr. He).