The SCA2-63K/Z solenoid valve is classified by function: water solenoid valve, steam solenoid valve, refrigeration solenoid valve, cryogenic solenoid valve, gas solenoid valve, fire solenoid valve, ammonia solenoid valve, gas solenoid valve, liquid solenoid valve, micro solenoid valve, pulse solenoid valve, hydraulic solenoid valve, normally open solenoid valve, oil solenoid valve, DC solenoid valve, high-pressure solenoid valve, explosion-proof solenoid valve, etc. From a national perspective, due to the different population densities and industrial water usage ratios in various cities, the total water supply for the same pipeline length can vary by 2 times or even more. Therefore, the same amount of leakage, in the city with the highest water usage, the leakage rate is statistically 19% or even more. Thus, the expression of leakage per unit length of pipe per unit time is relatively more reasonable. Valve island leak detection instruments are also an important part of leakage control. The valve island is also the main equipment for leak detection, which can correctly detect some difficult-to-inspect leaks, because it needs to contact the pipeline within a certain effective distance, therefore, it is suitable for checking smaller diameter pipes. The underground radar detector does not need to contact the pipeline, and the inspection speed is high, it can not only detect leaks but also check other functions such as pipeline settlement, appropriately selecting leak detection instruments, timely reducing leakage is an effective remedy for water supply safety. Lowering excessively high pipeline pressures is a necessary means to ensure water supply safety.DSBC-100-400-PPVA-N3, plastic air tube PUN-H-10X1,5-NTpolyurethane air tube PUN-16X2,5-SI, pressure reducing valve LR-M2-N1/4-07Gpressure reducing valve LR-3/4-D-7-O-MAXI-NPT, GRLA-1/8-QS-4-RS-DAEVULQZ-40-25-A-P-A, DSBC-63-40-PPVA-N3,DSBC-100-100-PPSA-N3, DGC-K-25-1600-PPV-A-GKDGC-32-1650-G-PPV-A, pressure reducing valve LR-M2-G3/8-07pressure regulating valve LRBS-D-O-MIDI, VN-05-M-T2-PI2-VI2-RI2GRLA-1/4-QS-8-RS-D, DSBC-40-30-PPSA-N3DSBC-40-300-PPSA-N3, DGC-K-32-200-PPV-A-GK,DGC-K-63-1000-PPV-A-GK, D series lockable pressure reducing valve LRS-1/2-D-7-O-DI-MAXIlockable pressure reducing valve LRS-1/4-S-B, pressure reducing valve LR-M2-N1/4-07GKM series pressure reducing valve LRB-M2-N1/2-04, vacuum suction cup ESV-60-SUvacuum suction cup ESV-80-BS, DFM-63-160-P-A-GF
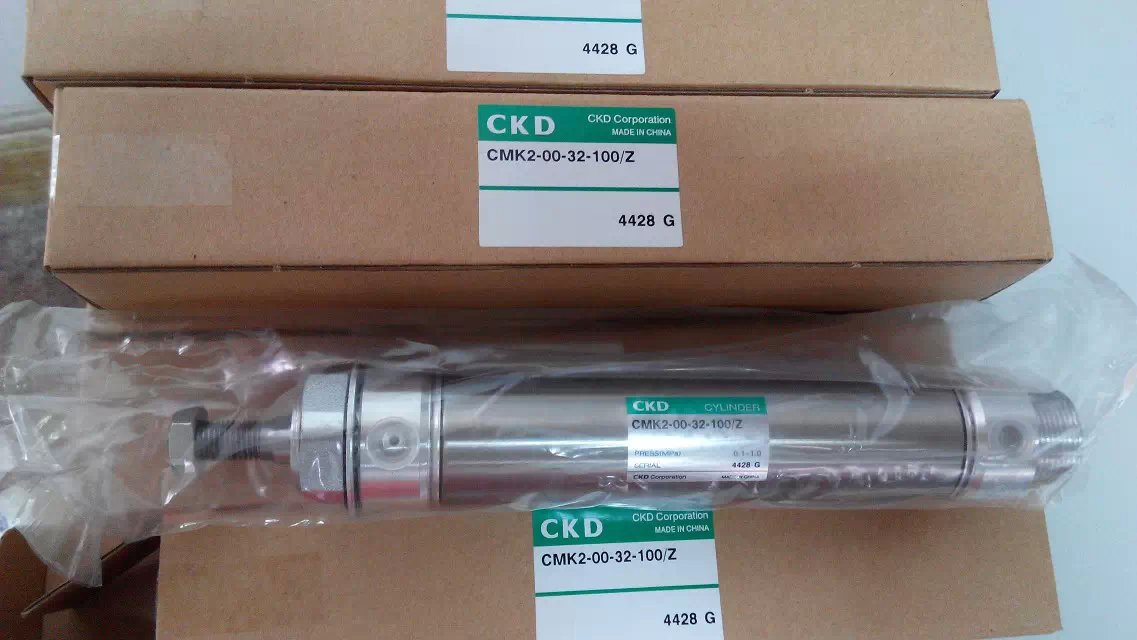
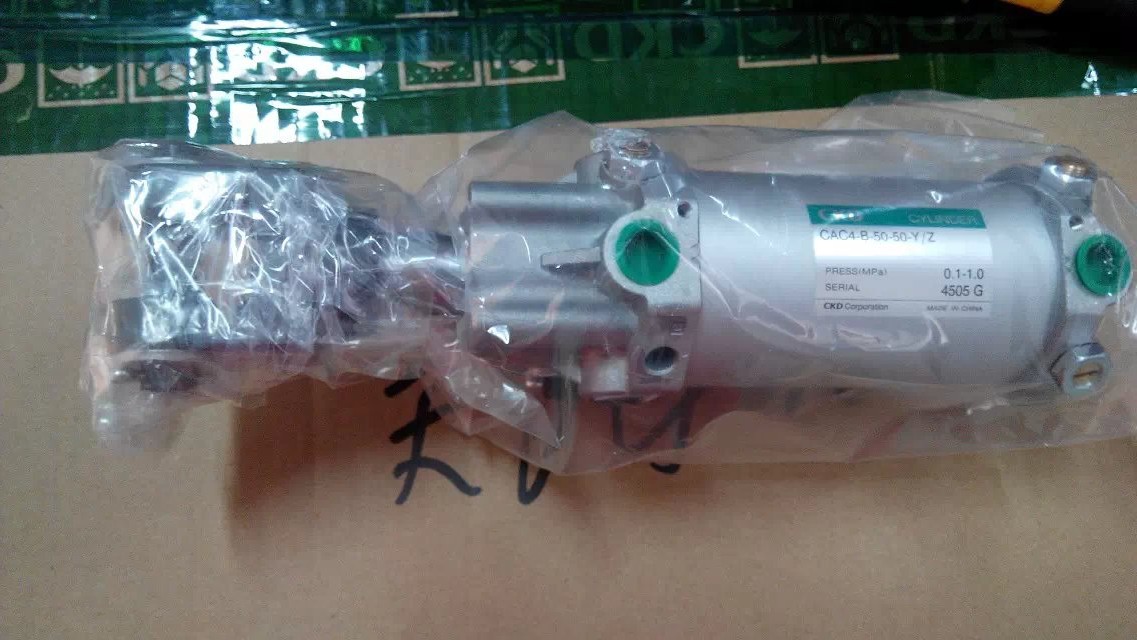
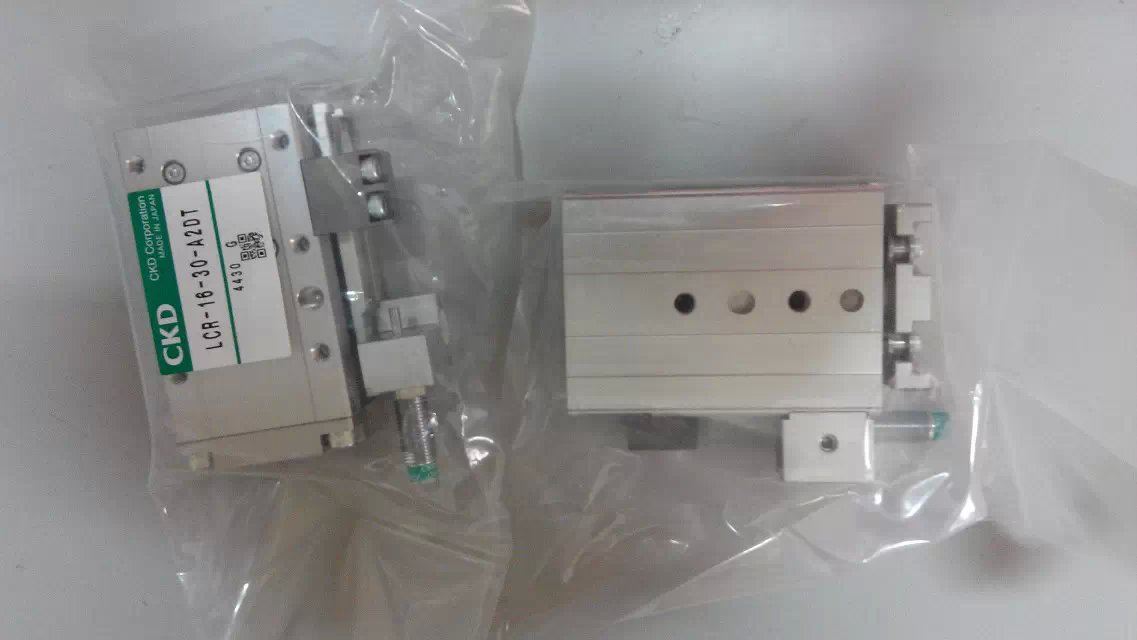
Medium-sized cylinder SCA2-63K/Z belongs to the Air Pressure Cylinders series under CKD company, model number SCA2-63K/Z. To purchase or inquire about Medium-sized cylinder SCA2-63K/Z, you can directly contact 158 0047 0089 (Mr. He).